Table of Contents
Introduction
The Universal Recycling Law (Act 148) was passed by the Vermont Legislature in 2012, banning recyclables and organic materials from the landfill. This law is just one major step in a larger goal to better handle waste in Vermont. The State of Vermont deploys several programs through the Agency of Natural Resources Department of Environmental Conservation (DEC) and the Agency of Agriculture, Food, and Markets (AAFM) which provide different strategies for managing waste. Please note this page does not encompass all waste management strategies, but is intended to provide guidance and support for those who are looking to manage organic waste on farms. To determine whether a specific operation is considered a 'farm', please refer to the RAPs. For more in-depth information, please refer to each program's specific webpage or reach out to the designated contact person(s).
Waste Management Matrix
This matrix is designed to identify applicable programs to manage a variety of organic waste types. The top row includes a list of waste types; you can click on each waste type to see their definition at the bottom of the page. The left column includes a list of management strategies. If a type of waste is eligible for a specific management strategy, the applicable programs will be listed in the corresponding cell.
|
|
Animal Mortalities |
Imported Biosolids |
Short Paper Fiber and Wood Ash |
|||||||
|
Land Application |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Manure Pit |
No program needed |
RAPs (if managed on-site where waste was produced) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
On-Farm Digester |
No program needed |
RAPs (if managed on-site where waste was produced) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Commercial Digester |
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Agricultural Composting |
No program needed |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
Commercial Composting |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
Sewage, Sludge, Biosolids, and Septage Treatment, Storage, and Transfer Facilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Organic Solid Waste Recovery Facility |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Distribution to the general public (after treatment) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Animal Feed |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
Food Residuals Drop Off Location |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-Sewage Wastewater System |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
On-farm burial |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Waste Management Programs:
Each of the following program sections contain a flowchart demonstrating the process for utilizing that specific program. The blue boxes represent applicant steps; the green boxes represent agency steps; the grey boxes represent neutral steps; the dotted arrows represent conditional steps. Some of the program sections contain a second flowchart to provide additional guidance for more complex waste eligibilities.
Agricultural Residuals Management Program (ARM):
This program, which is ran by the Agency of Agriculture, Food, and Markets, allows small farms to import up to 2,000 cubic yards per year of food residuals or food processing residuals for the production of compost, provided that the compost is either principally used on the farm where it is produced, or the compost is produced on a small farm that raises or manages poultry.
Waste eligibility:
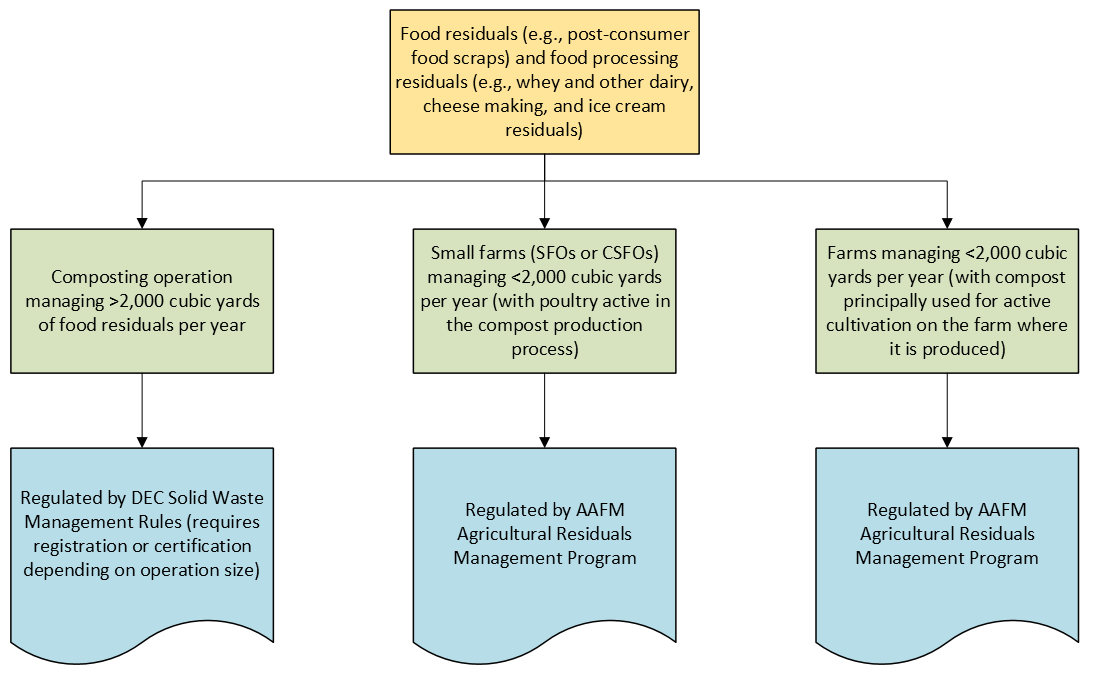
Process map:
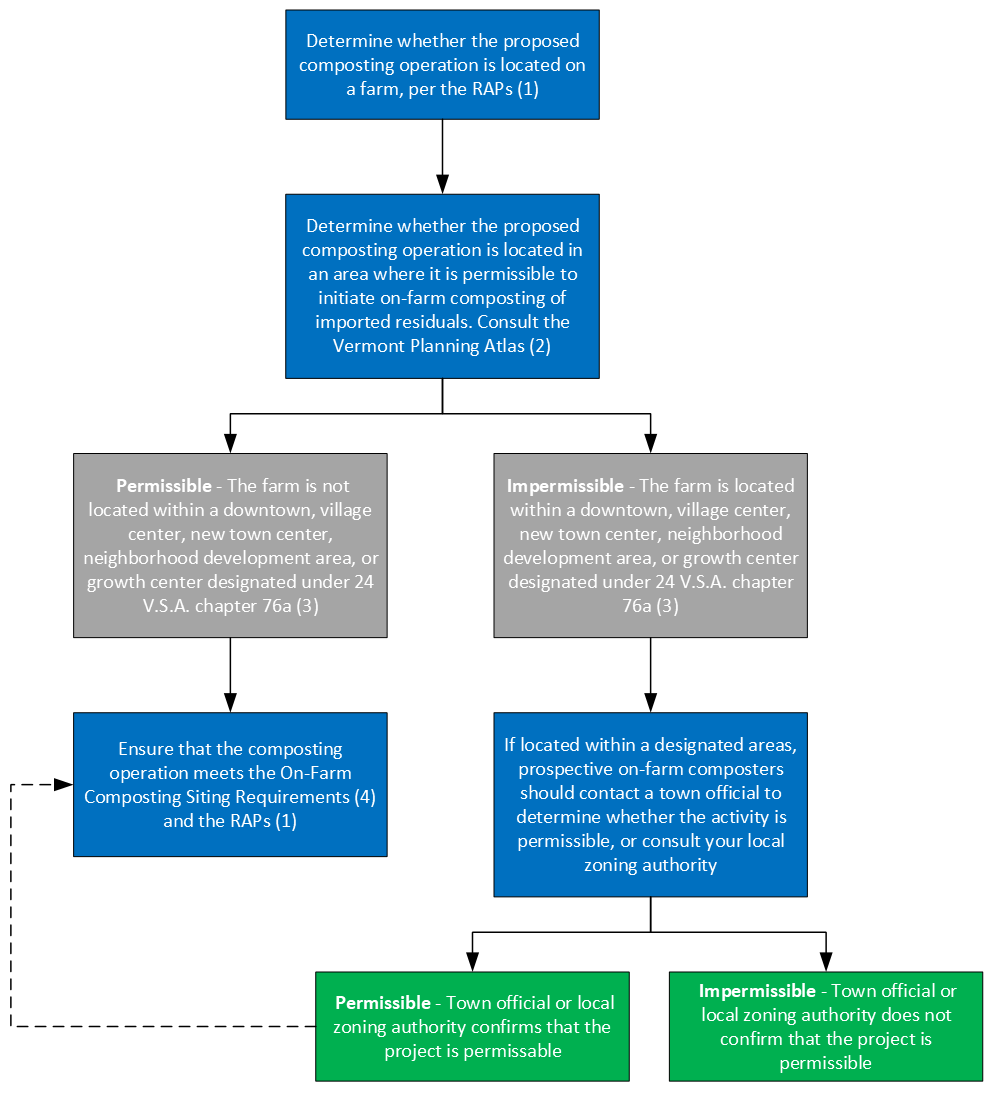
- Required Agricultural Practices Rule
- Section 3: Farm determination
- This program is only applicable for farming operations
- Vermont Planning Atlas
- 24 V.S.A. Chapter 76a
- On-Farm Composting Siting Requirements
Important forms and resources:
Agricultural Residuals Management Program webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Act 41 S.102 Section 7: An act relating to the regulation of agricultural inputs for farming
- 6 V.S.A. Chapter 218: Agricultural Residuals Management
- 6 V.S.A. Chapter 28: Fertilizer and Lime
- 10 V.S.A. Chapter 159: Waste Management
- § 6602
Contacts:
General Inquiries and Consumer Concerns: 802-828-2430 | AGR.helpdesk@vermont.gov
See program webpage or Staff Directory by Division for individual contacts
Return to Top
Commercial Feed Program (CF):
This program, which is ran by the Agency of Agriculture, Food, and Markets, provides for the registration, inspection and analysis of all commercial feed and pet food products sold in Vermont.
Waste eligibility:
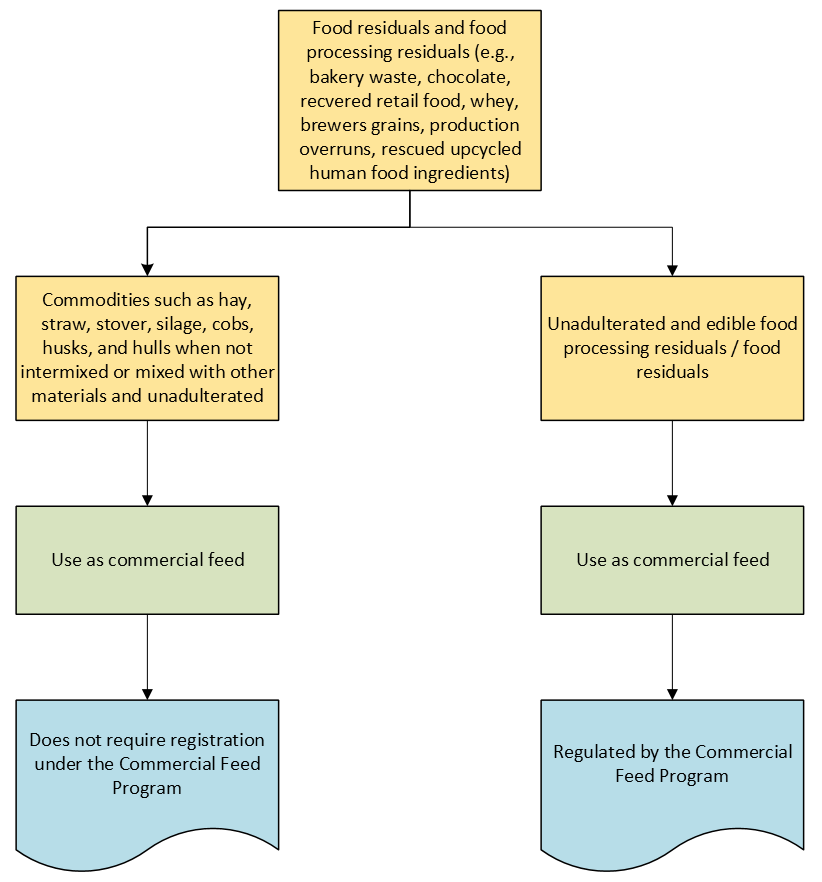
Process map:
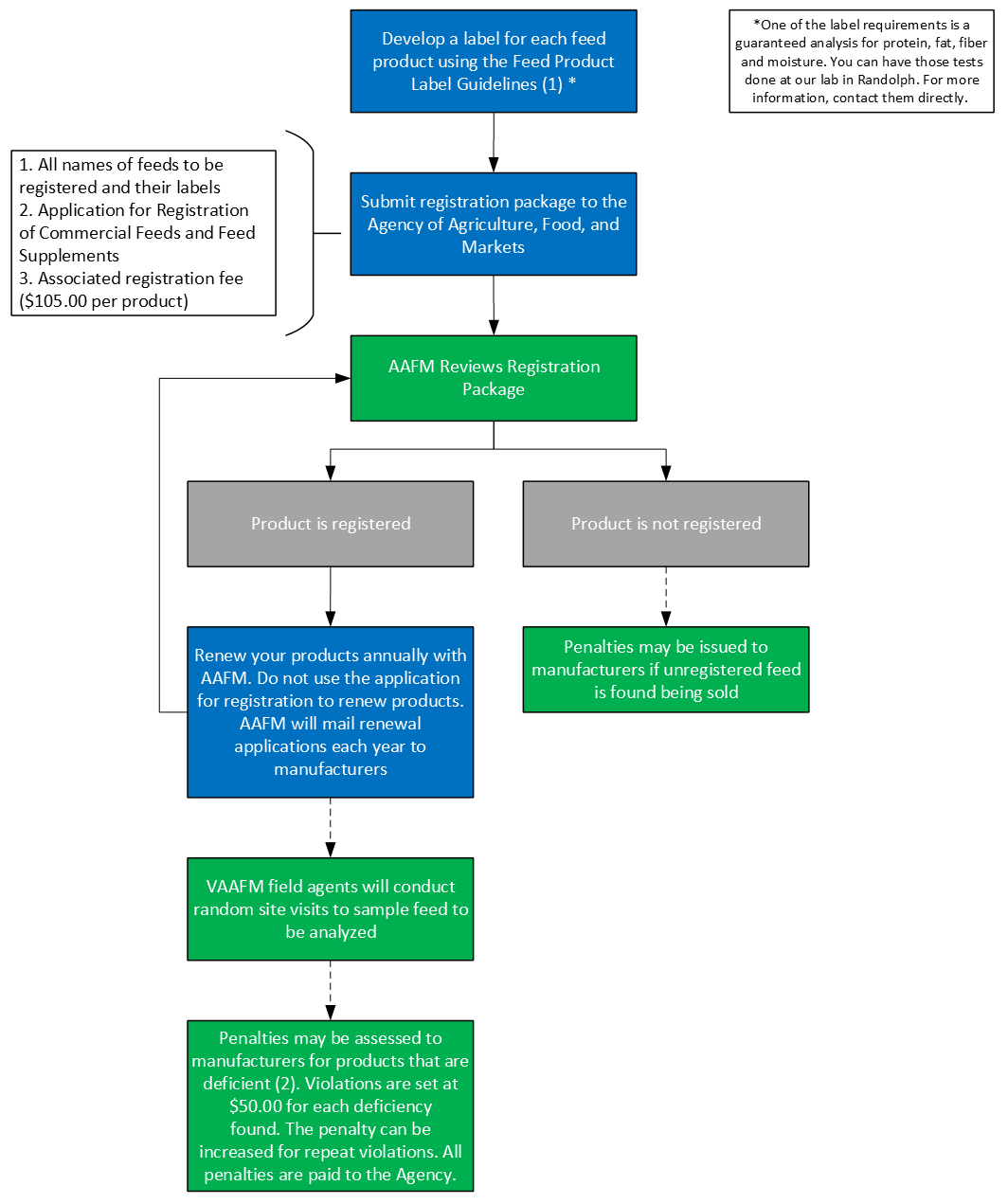
- Feed Product Label Guidelines
- 6 V.S.A. Chapter 26 §333: Commercial Feeds, Penalties
Important forms and resources:
Commercial Feed Program webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Relevant regulations and legislation:
- 6 V.S.A. Chapter 26: Commercial Feeds
- Vermont Feed Regulations
- Vermont pet Food Regulations
- Regulations from The Association of American Feed Control Officials (AAFCO)
Contacts:
Questions regarding registration and labeling: AGR.FeedSeedFert@vermont.gov
Sample Receiving: 802-461-3363 | AGR.VAEL@vermont.gov
General Inquiries and Consumer Concerns: 802-828-2430 | AGR.helpdesk@vermont.gov
See program webpage or Staff Directory by Division for individual contacts
Return to Top
Custom Applicator Certification Program (CAC):
This program, which is ran by the Agency of Agriculture, Food, and Markets, includes training and certification requirements for custom manure applicators that operate within the State of Vermont.
Waste eligibility:
This program applies to the spreading of manure only. Pesticide applicators should obtain a Pesticide Applicator Certification.
Process map:

Important forms and resources:
Custom Applicator Certification Program webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Online UVM Training Course and Certifying Exam
Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Act 64: Vermont Clean Water Act
- 6 V.S.A. Chapter 215: Agricultural Water Quality
- Subchapter 9: Certification of Custom Applicators of Manure or Agricultural Waste
- § 4988
- RAPs Section 10: Custom Applicator Certification
Contacts:
For questions regarding application and reporting: AGR.WQpermits@vermont.gov
General Inquiries and Consumer Concerns: 802-828-2430 | AGR.helpdesk@vermont.gov
See program webpage or Staff Directory by Division for individual contacts
Return to Top
Indirect Discharge Program (IDP):
This program, which is run by the Department of Environmental Conservation, regulates the land application of food processing wastes applied to fields by the generator of the wastes.
Waste eligibility:
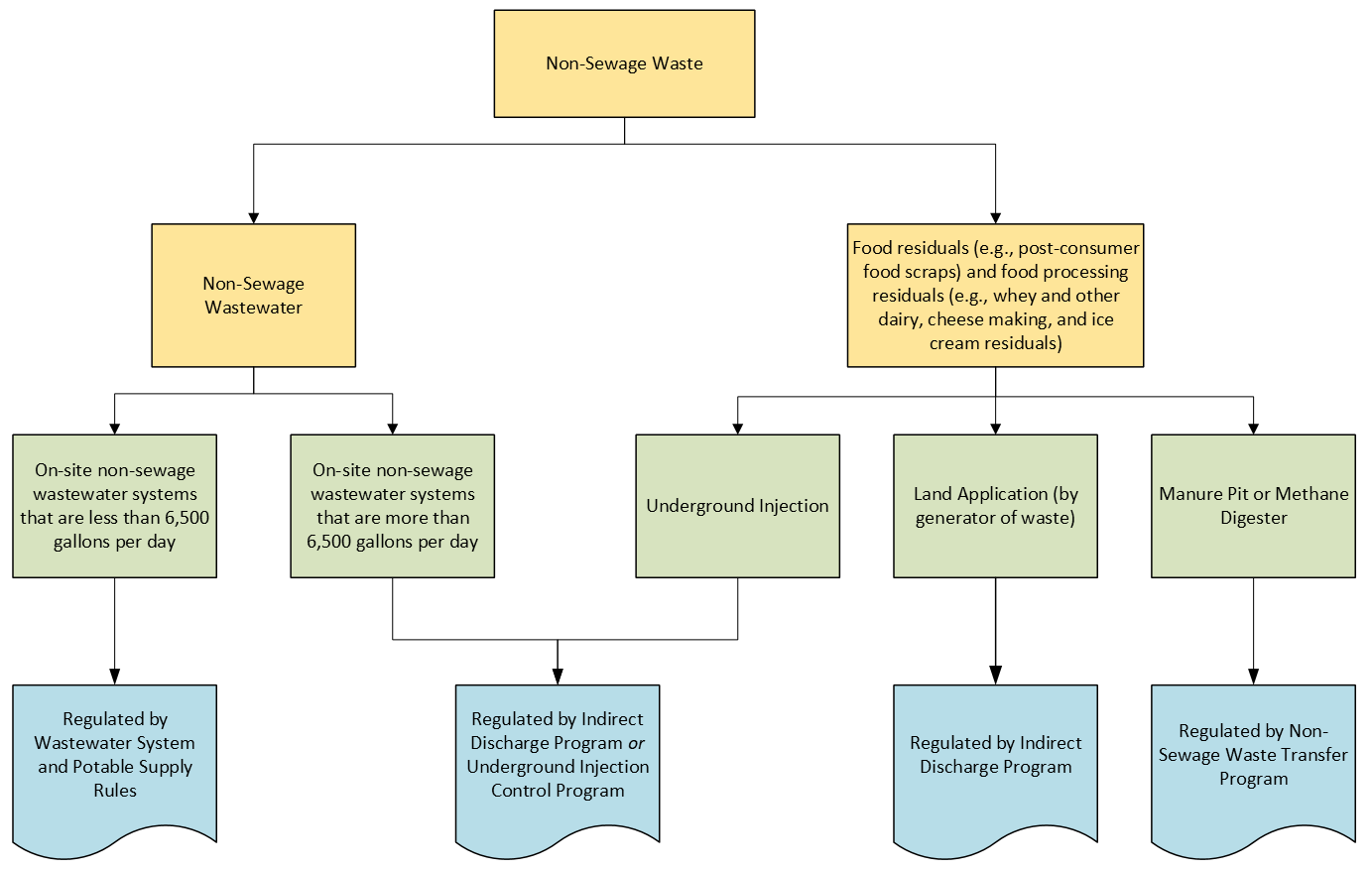
Process map:
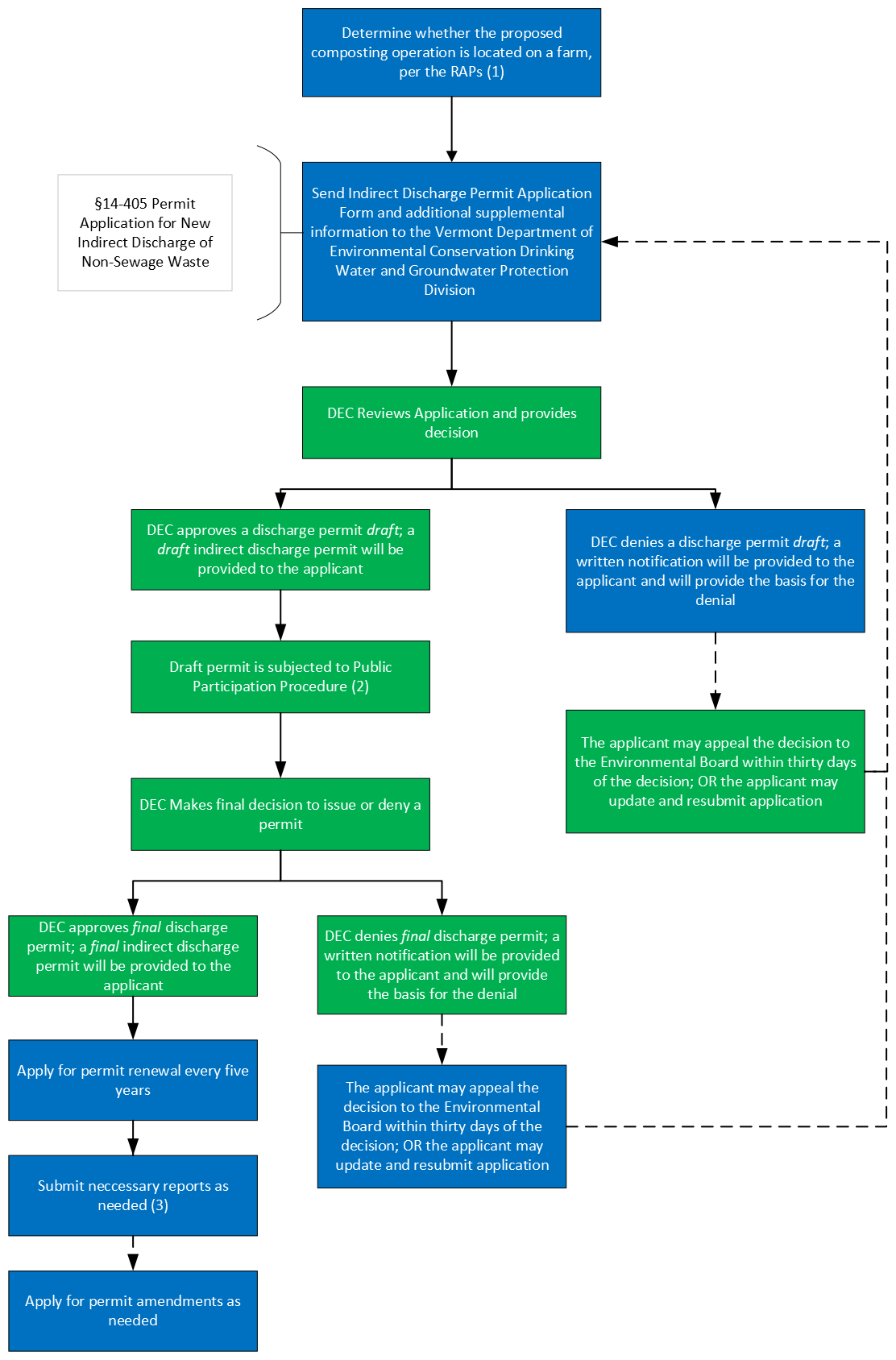
- Required Agricultural Practices Rule
- Section 3: Farm determination
- This program is only applicable for non-farming operations
- Public Participation Procedure - §14-504 of the Environmental Protection Rules
- Reporting - §14-801-§14-805 of the Environmental Protection Rules
Important forms and resources:
Indirect Discharge Program webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Environmental Protection Rules
- Chapter 1: Wastewater System and Potable Water Supply Rules
- Chapter 6: Solid Waste Management Rules
- Chapter 14: Indirect Discharge Rules
- 10 V.S.A. Chapter 47: Water Pollution Control
- §1272
- §1263
- Vermont Guidelines for the Land Application of Dairy Processing Wastes
Contacts:
Drinking Water & Groundwater Protection Division: 802-828-1535
Return to Top
Non-Sewage Waste Transfer Program (NSW):
This program, which is run by the Agency of Agriculture, Food, and Markets, regulates the generators or haulers of non-sewage waste who are transporting or arranging for the transport of non-sewage waste to a farm for deposit in a manure pit or for use as an input in a methane digester.
Process map:
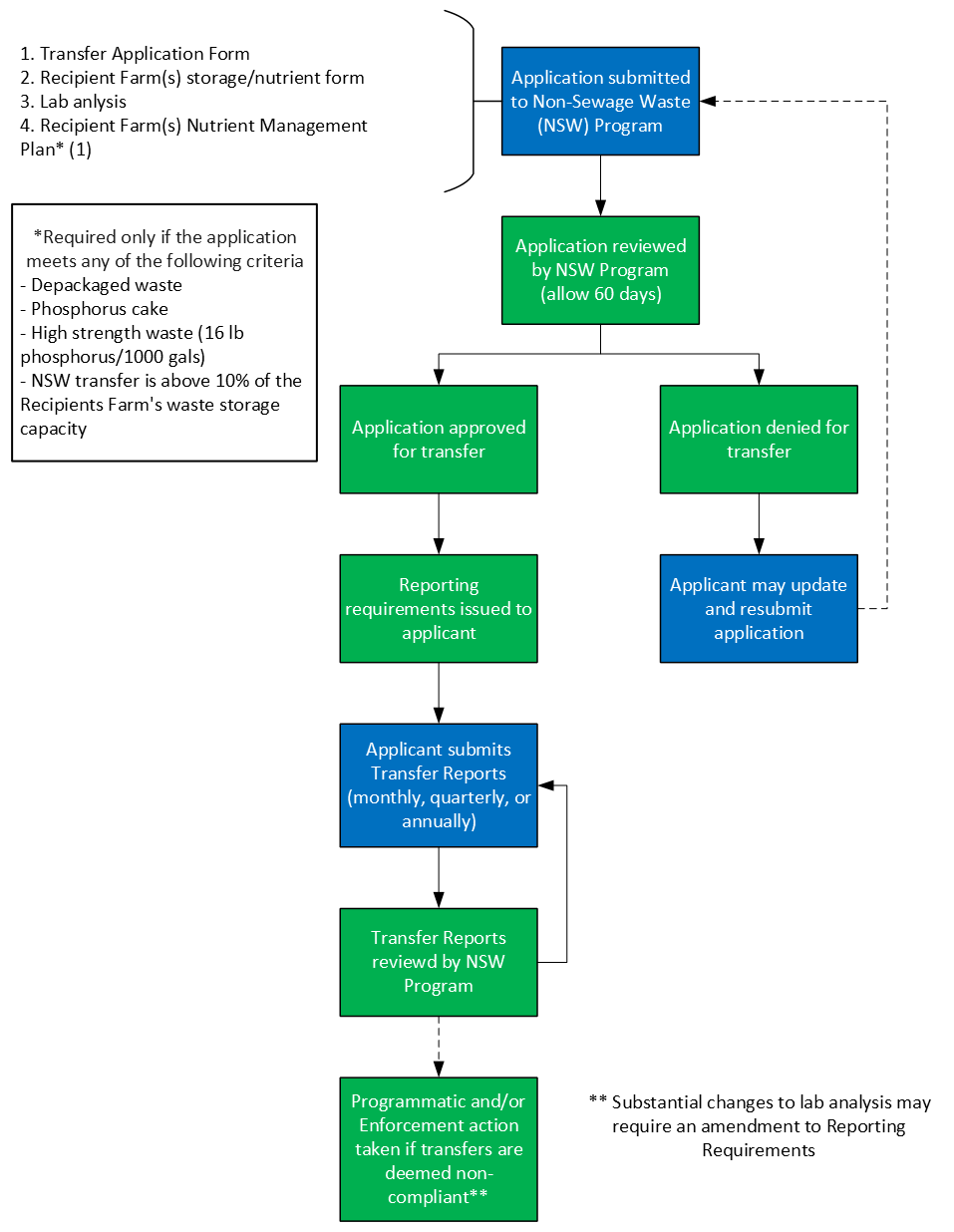
- Nutrient Management Plans – Information available on the VAAFM website
Important forms and resources:
Non-Sewage Waste Transfer Program webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Act 129 (2020): An act relating to miscellaneous agricultural subjects
Contacts:
For questions regarding application and reporting: AGR.WQpermits@vermont.gov
General Inquiries and Consumer Concerns: 802-828-2430 | AGR.helpdesk@vermont.gov
See program webpage or Staff Directory by Division for individual contacts
Return to Top
Required Agricultural Practices (RAPs):
The RAPs are not a specific program, but rather a set of standards to which all types of farms must be managed to reduce the impact of agricultural activities to water quality. The RAPs include required practices and management strategies, some of which apply to all farms and some of which are specific to certain sizes of operation or to certain environmental factors.
Important forms and resources:
Required Agricultural Practices webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Required Agricultural Practices Rule
- Section 3: Farm determination
- Section 6.08: Location and setbacks for composting or burial of animal mortalities on farms
Contacts:
For questions regarding the regulatory statute:
- Laura DiPietro, Director Water Quality Division: 802-595-1990 | laura.dipietro@vermont.gov
General Inquiries and Consumer Concerns: 802-828-2430 | AGR.helpdesk@vermont.gov
See program webpage or Staff Directory by Division for individual contacts
Return to Top
Residuals and Emerging Contaminants Program (REC):
This program, which is run by the Department of Environmental Conservation, oversees the management of residual materials, industrial and municipal wastes with the potential to be recycled.
Waste eligibility:
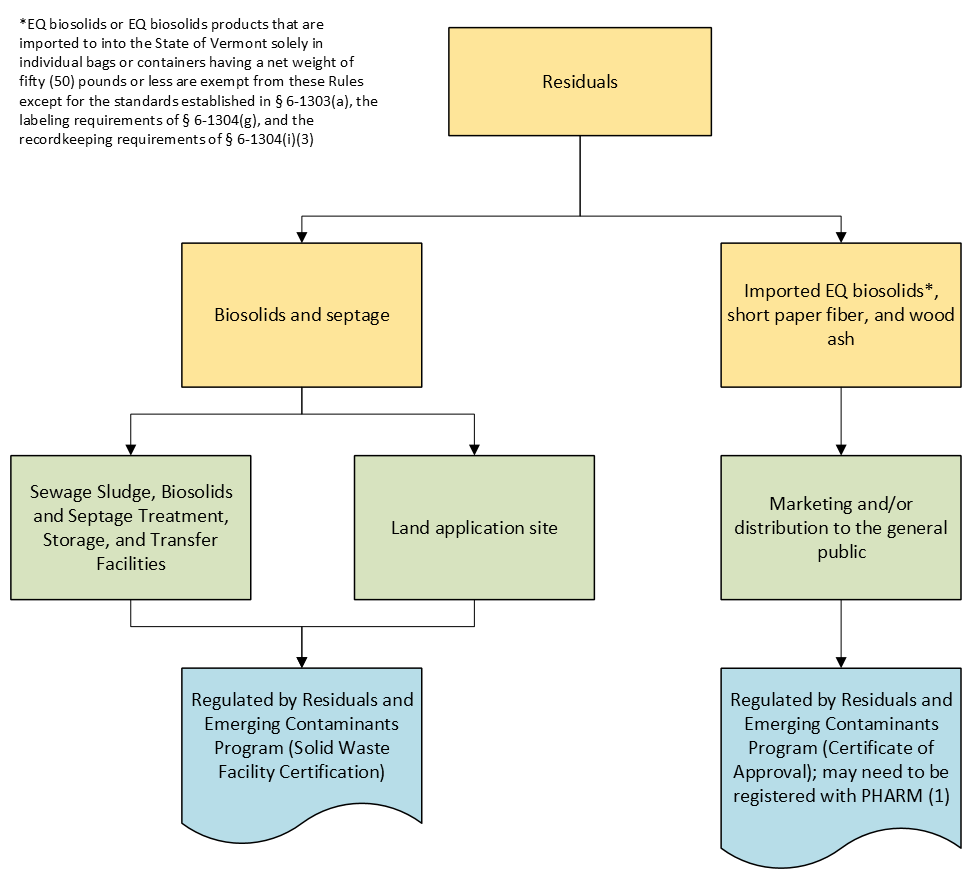
Solid Waste Facilities:
Solid Waste Facility Certification Process map:
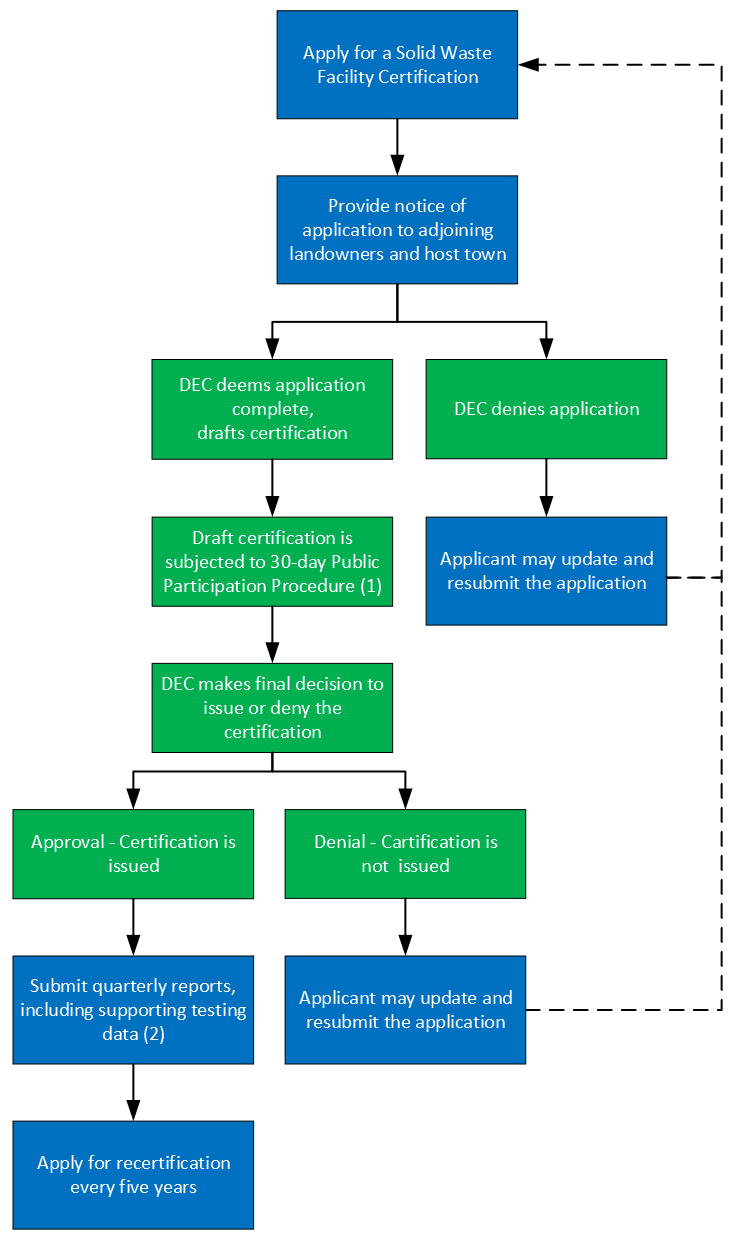
- Public Participation Procedure - § 6-601 (c) and § 6-602 (c) of the Solid Waste Rules
- Reporting and recordkeeping
- Residuals Quarterly Reporting: use the electronic reporting system to report activities associated with sludge/biosolids, septage, short paper fiber, and wood ash management. For those without access to a computer or internet, a waiver is available. Please contact the Residuals Management Program for more information about the waiver process.
- § 6-1308 of the Solid Waste Management Rules
Solid Waste Facility Important forms and resources:
Residuals and Emerging Contaminants Program webpage - see here for application forms and reporting info
Procedure
Solid Waste Facility Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Solid Waste Management Rules
- 10 V.S.A. Chapter 48: Groundwater Protection
Certificates of Approval:
Certificate of Approval Process map:
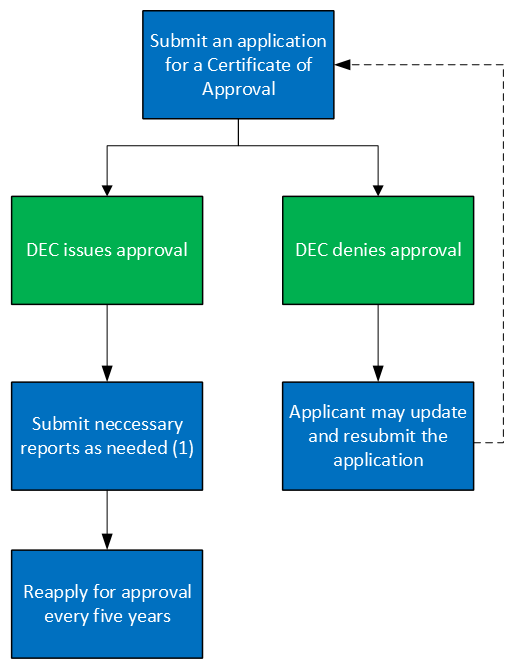
- Reporting and recordkeeping
- Residuals Quarterly Reporting: use the electronic reporting system to report activities associated with sludge/biosolids, septage, short paper fiber, and wood ash management. For those without access to a computer or internet, a waiver is available. Please contact the Residuals Management Program for more information about the waiver process.
- § 6-1308 of the Solid Waste Management Rules for sludge management facilities
- § 6-1304 (h) and (i) of the Solid Waste Management Rules for EQ biosolids
Certificate of Approval Important forms and resources:
Residuals and Emerging Contaminants Program webpage - see here for application forms and reporting info
Procedure
- Wood Ash Management Procedure (pdf)
- Short Paper Fiber Management Procedure (pdf)
- Interim Strategy for Mitigating PFAS Risks Associated with Residuals Management
Certificate of Approval Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Solid Waste Management Rules
- § 6-1303 (c)
Contacts:
DEC Waste Management and Prevention Division: 802-828-1138
Return to Top
Solid Waste Program (SWP):
This program, which is run by the Department of Environmental Conservation, implements Vermont's solid waste management rules by providing certifications to operate various types of solid waste management facilities.
Waste eligibility:
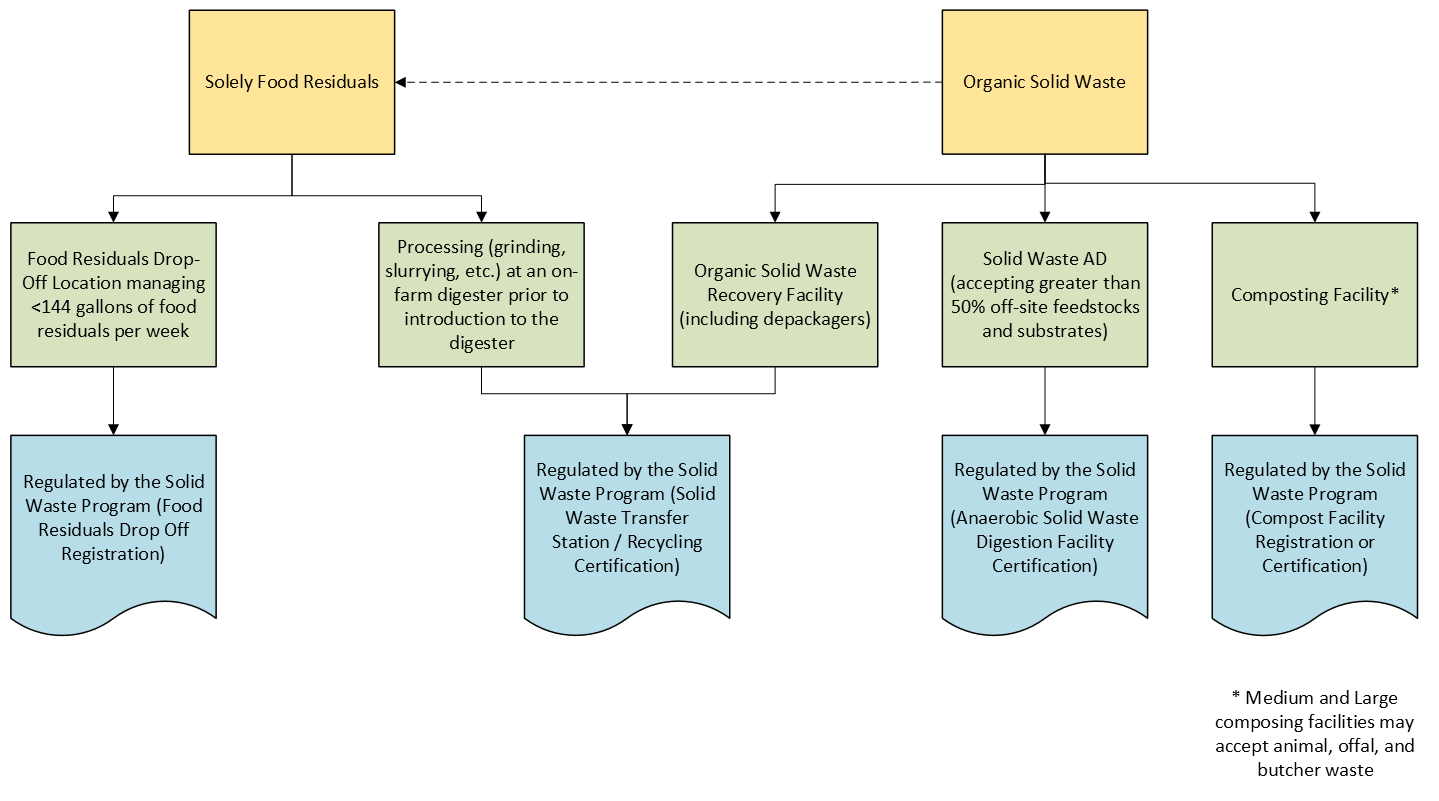
Anaerobic Digestion Facilities:
Anaerobic Digestion Facility Process map:
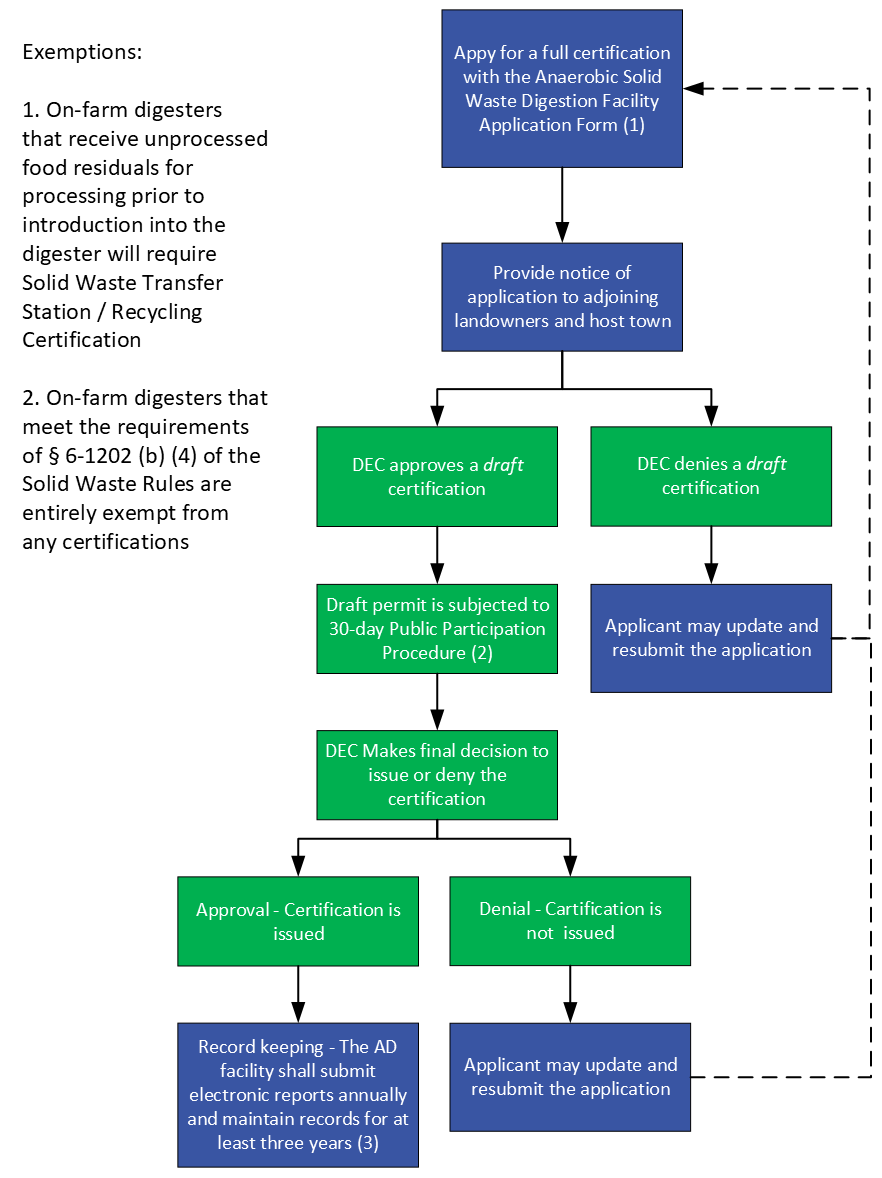
- Exemptions
- On-farm digesters that receive unprocessed food residuals for processing prior to introduction into the digester are exempt from this program and, instead, require Solid Waste Transfer Station / Recycling Certification
- On-farm digesters that meet the requirements of § 6-1202 (b) (4) of the Solid Waste Rules are entirely exempt from any certifications
- Public Participation Procedure - § 6-601 (c) of the Solid Waste Rules
- Recordkeeping - § 6-1207 (b) of the Solid Waste Rules
Anaerobic Digestion Facility Important forms and resources:
Solid Waste Program webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Anaerobic Digestion Facility Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Solid Waste Management Rules, Subchapter 12: Organic Solid Waste Management Facilities
Commercial Composting Facilities:
Commercial Composting Facility Process map:
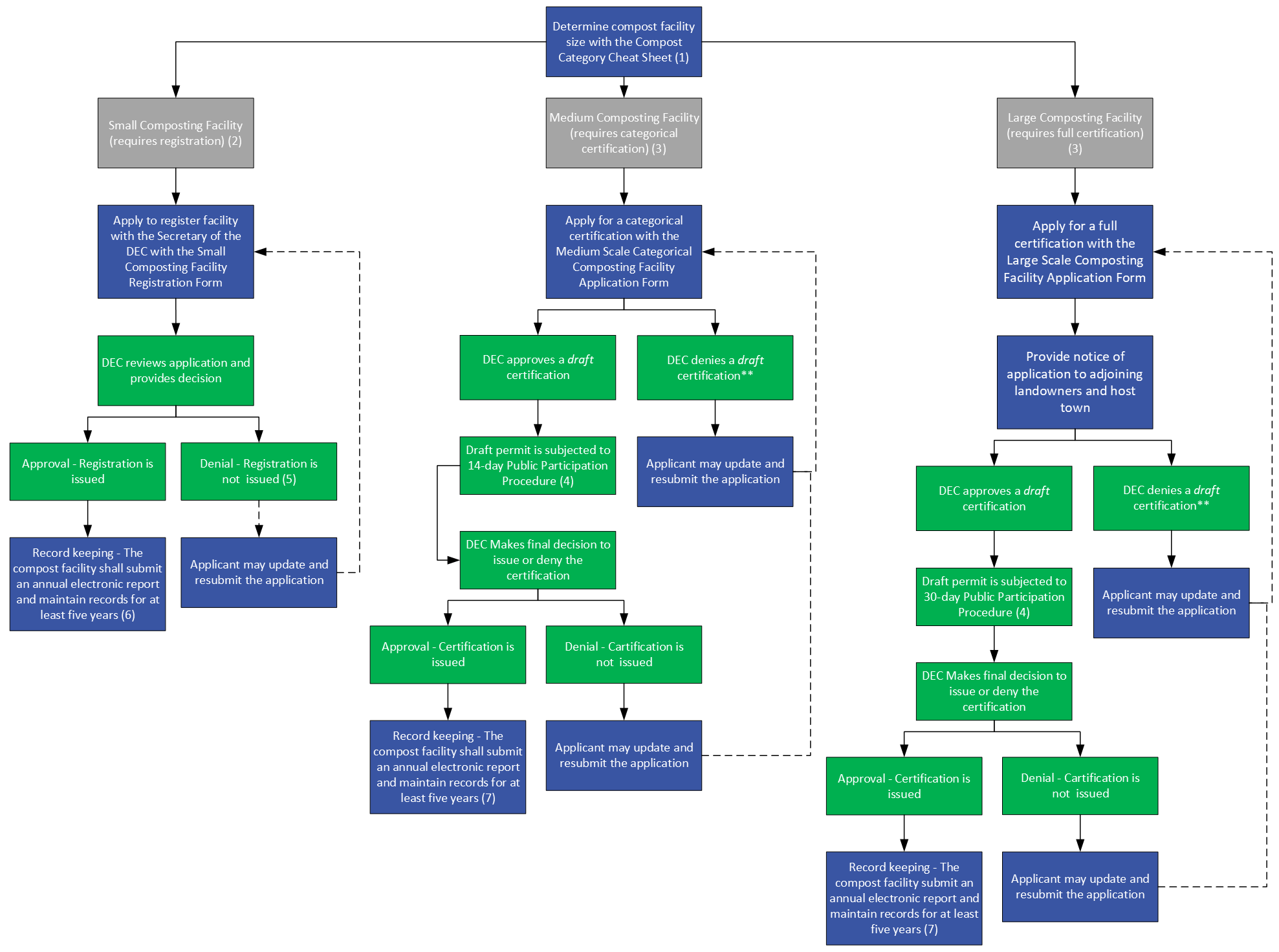
- Compost Category Cheat Sheet
- As part of the operating standards, a minimum of one person at the facility on any operating day shall have completed an Approved Compost Operator Training Course within six (6) months of filing the registration
- As part of the operating standards, a minimum of one person at the facility on any operating day shall have completed an Approved Compost Operator Training Course prior to registration
- Public Participation Procedure - § 6-601 (c) and § 6-602 (c) of the Solid Waste Rules
- If the proposed facility size, processes, activities, or the nature of the composting activities require additional review and oversight not provided by this section, the applicant may have to apply for a different certification
- Small Composting Facility Recordkeeping - § 6-1105 (d) (3) of the Solid Waste Rules
- Medium and Large Composting Facility Recordkeeping - § 6-1110 of the Solid Waste Rules
Composting Facility Important forms and resources:
Solid Waste Program webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Miscellaneous:
Composting Facility Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Solid Waste Management Rules, Subchapter 11: Compost Facilities
Food Residuals Drop Off:
Food Residuals Drop Off Process map:
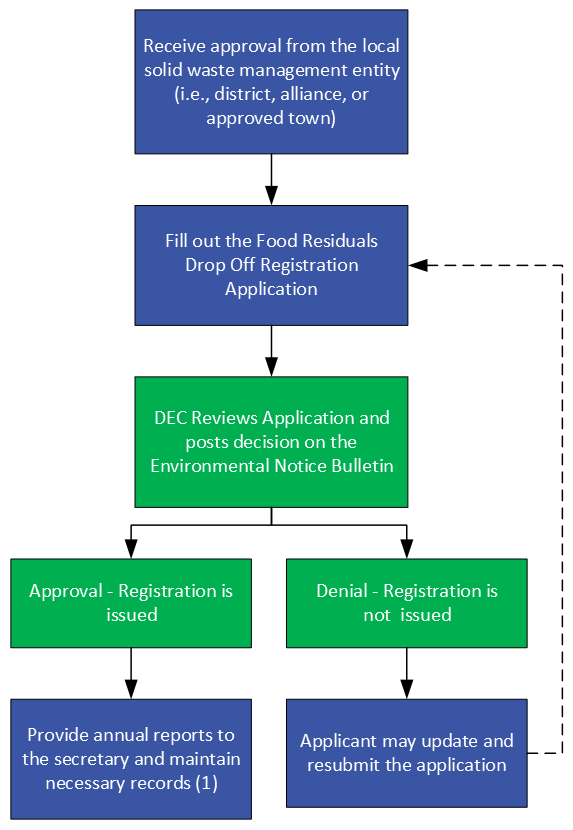
- Recordkeeping - § 6-707of the Solid Waste Rules
Food Residuals Drop Off Important forms and resources:
Solid Waste Program webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Food Residuals Drop Off Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Solid Waste Management Rules, Subchapter 12: Organic Solid Waste Management Facilities
Transfer Stations:
Transfer Station Process map:
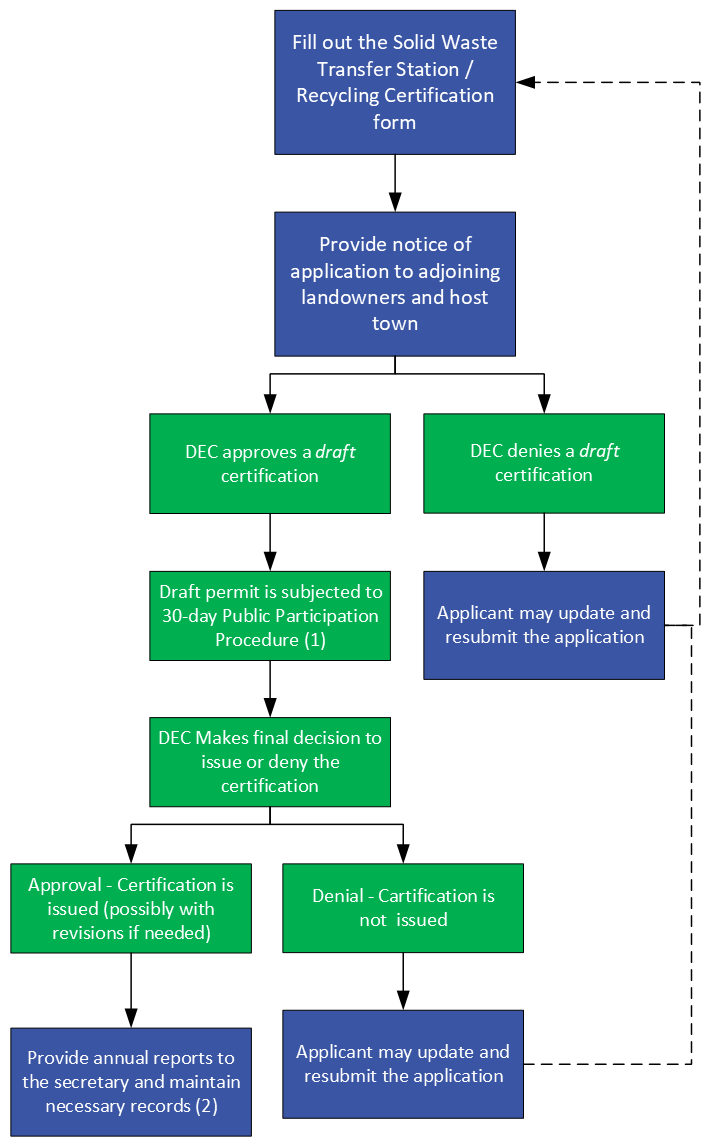
- Public Participation Procedure - § 6-601 (c) of the Solid Waste Rules
- Recordkeeping - § 6-707of the Solid Waste Rules
Transfer Station Important forms and resources:
Solid Waste Program webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Transfer Station Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Solid Waste Management Rules, Subchapter 9: Storage, Transfer, Recycling and Processing Facilities
Contacts:
- Ben Gauthier, Solid Waste Management Program: 802-522-5080 | benjamin.gauthier@vermont.gov
General Inquiries and Consumer Concerns: 802-828-2430 | AGR.helpdesk@vermont.gov
See program webpage or Staff Directory by Division for individual contacts
Return to Top
Underground Injection Control Program (UIC):
This program, which is run by the Department of Environmental Conservation, regulates floor drains that discharge fluid wastes to the soil or groundwater.
Waste eligibility:
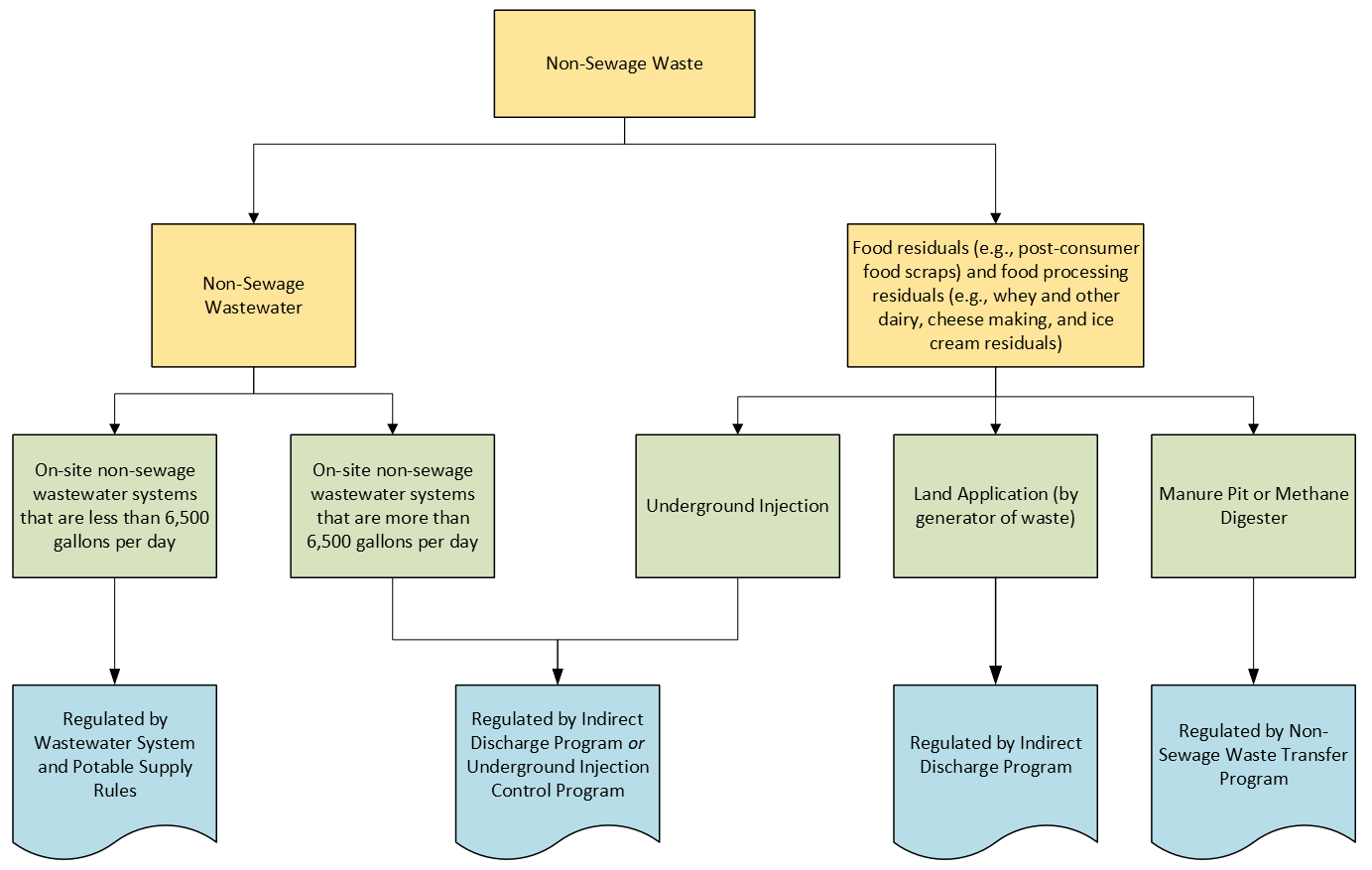
Process map:
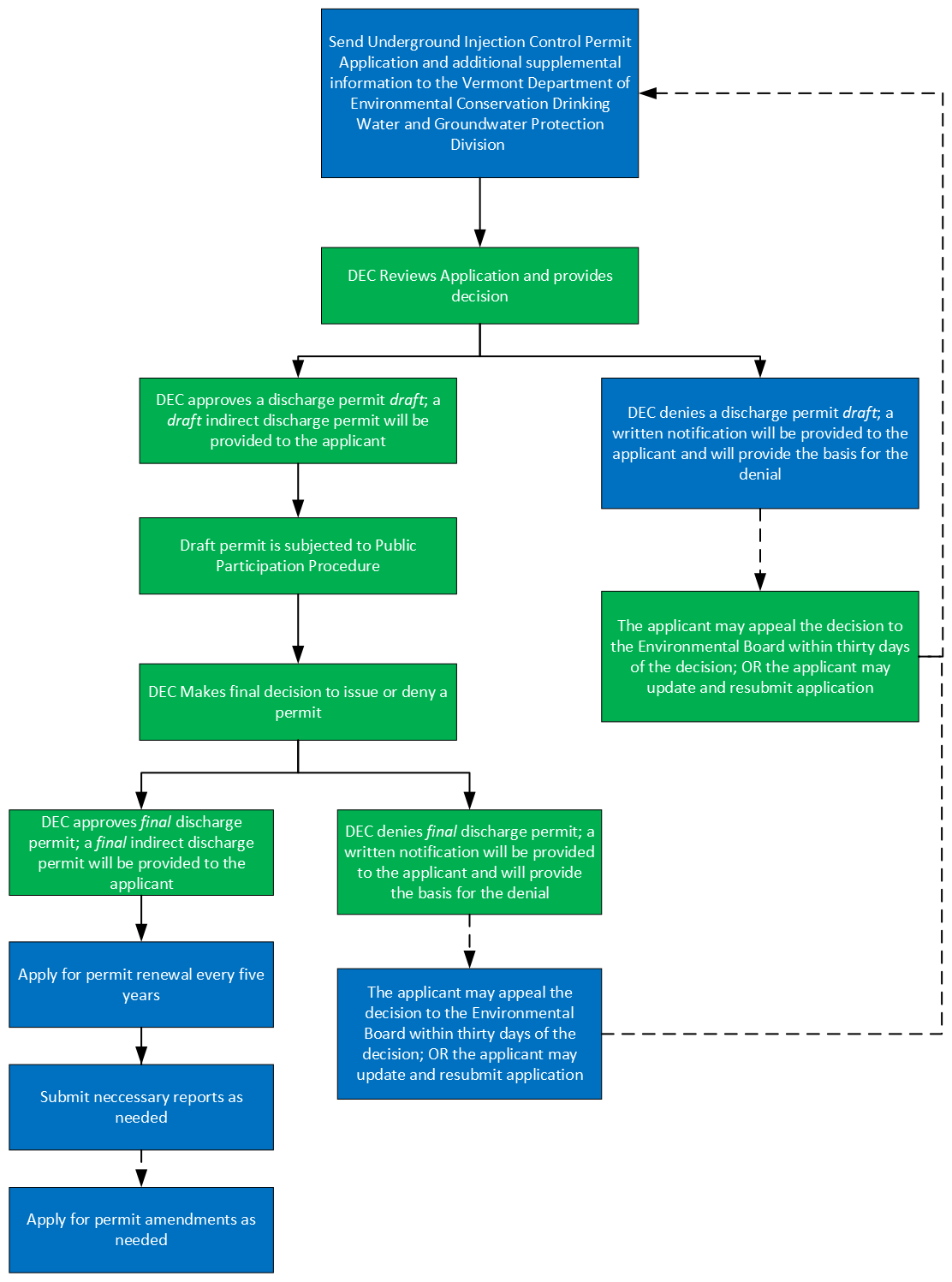
Important forms and resources:
Underground Injection Control Program Webpage - see here for important information, forms, and specific contacts
Relevant regulations and legislation:
- Environmental Protection Rules
- Chapter 1: Wastewater System and Potable Water Supply Rules
- Chapter 6: Solid Waste Management Rules
- Chapter 11: Underground Injection Control Regulations
- Chapter 12: Groundwater Protection Rule and Strategy
- 10 V.S.A. Chapter 47: Water Pollution Control
- §1272
- §1263
Contacts:
Drinking Water & Groundwater Protection Division: 802-828-1535
Return to Top
Definitions:
“Agricultural residuals” means the remaining organic material left over from food production or other processes that are either generated by a farm or imported onto a farm for farming purposes. – Agricultural Residuals Management Program
“Biosolids” means sewage sludge derived, in whole or in part, from domestic wastes which have been subjected to a treatment process for the reduction of pathogens and have been demonstrated to meet the applicable requirements of these Rules for contaminant concentrations, vector attraction reduction, and pathogen reduction, such that the material has been approved by the Secretary for application to the land under a site specific solid waste facility certification – Solid Waste Management Rules
“Commercial feed” means all materials except whole seeds unmixed or physically altered entire unmixed seeds, when not adulterated… that are distributed for use as feed or for mixing in feed. The Secretary by regulation may exempt from this definition, or from specific provisions of this chapter, commodities such as hay, straw, stover, silage, cobs, husks, hulls, and individual chemical compounds or substances when such commodities, compounds, or substances are not intermixed or mixed with other materials and are not adulterated – 6 V.S.A. Chapter 26: Commercial Feeds
"Compost" means a stable humus-like material produced by the controlled aerobic biological decomposition of organic matter through active management, but shall not mean sewage, septage, or materials derived from sewage or septage. – 6 V.S.A. Chapter 218: Agricultural Residuals Management, 10 V.S.A. Chapter 47: Water Pollution Control, 10 V.S.A Chapter 159: Waste Management, Solid Waste Management Rules
“Food processing residual” means the remaining organic material from a food processing plant and may include whey and other dairy, cheese making, and ice cream residuals or residuals from any food manufacturing process excluding livestock or poultry slaughtering and rendering operations. “Food processing residuals” does not include food residuals from markets, groceries, or restaurants. - 6 V.S.A. Chapter 218: Agricultural Residuals Management, Solid Waste Management Rules
“Food Processing Waste” means wastewater that is generated from the manufacturing of a food or beverage product and that consists of washwater or residual food or beverage waste from food processing facilities making such products as dairy products, beer, wine, spirits, maple syrup and candy, and microwave dinners. “Food processing waste” does not include waste from slaughterhouse facilities or rendering operations, wastewater associated with the washing of unaltered fruits, vegetables or other farm produce, or food or food preparation wastewater from food markets, grocery stores, food store, delis or restaurants" - Wastewater System and Potable Water Supply Rules
"Food residuals” means source separated and uncontaminated material that is derived from processing or discarding of food and that is recyclable or compostable. “Food residuals” may include pre-consumer and postconsumer food scraps.
- “Food residuals” include meat and meat-related products when the disposition of the products is managed on a farm. - 6 V.S.A. Chapter 218: Agricultural Residuals Management
- “Food residual” does not mean meat and meat related products when the food residuals are composted by a resident on site. – 10 V.S.A. Chapter 159: Waste Management, Solid Waste Management Rules
“Food Residual Drop-Off” means a registered facility that is not located at a certified solid waste facility and is approved only for the collection of food residuals. – Solid Waste Management Rules
“Implementation Plan” means a municipal or Solid Waste Management Entity’s plan which is adopted and found to be consistent with the State Material Management Plan. This plan must include all the elements required for consistency with the State plan and an applicable regional plan and shall be approved by the Secretary. – Solid Waste Management Rules
“Indirect Discharge” means any discharge to groundwater, whether subsurface, land-based, or otherwise - 10 V.S.A. Chapter 47: Water Pollution Control
“Land application” means the diffuse spreading of non-EQ biosolids and stabilized domestic septage on the land at a controlled application rate for the purpose of providing agricultural nutrients, improving soil structure, or reclaiming a site. - Solid Waste Management Rules
- Note: for programs through the agency of agriculture, land application applies to the spreading or application of agricultural wastes as opposed to solid wastes
“Non-Sewage Waste” means any waste other than sewage which may contain organisms pathogenic to human beings but does not mean stormwater runoff" – 6 V.S.A. Chapter 215: Agricultural Water Quality, Indirect Discharge Rules
“Organic Solid Waste” means any solid waste that is a carbon-based plant or animal material or byproduct thereof which will decompose into soil and is therefore free of non-organic materials and contamination. Examples of organic materials include food residuals, leaf and yard residuals, grass clippings, and paper products. Domestic waste (human and pet feces) is not included in this definition. – Solid Waste Management Rules
“Organic Solid Waste Recovery Facility” or “ORF” means a facility where organic solid wastes are collected, treated, and/or stored in preparation for transfer to an anaerobic digester or compost operation. This includes on-farm anaerobic digesters that process food residuals on-site prior to introduction to the digester. – Solid Waste Management Rules
“Processed food residuals” are food residuals which have been slurried into a condition which is suitable to being directly pumped into a holding tank. – Solid Waste Management Rules
“Residual Waste” or “Residuals” shall mean sewage sludge, biosolids, EQ biosolids, short paper fiber, wood ash, and drinking water treatment sludge. – Solid Waste Management Rules
“Septage” means the liquid or solid materials pumped from a septic tank that receives either commercial wastewater or industrial wastewater; or a mixture of commercial and domestic wastes, portable toilet waste, holding tank waste, cesspool waste, waste from Type III marine sanitation devices, or a mixture of grease and domestic waste removed from a grease trap during cleaning." - Solid Waste Management Rules
“Sewage Sludge” means any solid, semisolid, or liquid generated from a municipal, commercial, or industrial wastewater treatment facility or process treating any amount of domestic waste. - Solid Waste Management Rules
“Short paper fiber (SPF)” means a byproduct of paper manufacturing – paper fibers that are too short to bind together in the paper making process. SPF is a source of organic matter for soil amendments and helps reduce erosion when establishing vegetation on slopes. It is also used as animal bedding - Wastewater Treatment Sludge and Septage Management in Vermont
“Slaughterhouse Waste” means the residual liquid, inedible animal tissues and offal derived from the production of meat. Slaughterhouse waste is not a food residual. – Solid Waste Management Rules
“Sludge” means any solid, semisolid, or liquid generated from a municipal, commercial, or industrial wastewater treatment facility or process, water supply treatment plant, air pollution control facility or any other such waste having similar characteristics and effects. - Solid Waste Management Rules
“Wastewater” sanitary waste or used water from any building or structure or campground, including, but not limited to, carriage water, toilet water, shower and wash water, food processing wastewater, and process wastewater. Wastewater does not include stormwater - Wastewater System and Potable Water Supply Rules

